Latest Research Videos
Research Projects
3D Printing and Digital Fabrication
Cage-based Performance Capture
Video-based Appearance Stylization
Shape Reconstruction and Registration
Skeletal Captured Animation Interaction

|
3D printing is an ubiquitous technology employed to output fabricated real-world shapes
relying on fast prototyping. Digital fabrication designs physical objects
by processing their digital structures. we are interested in investigating algorithms
for hollowing, structural analysis, slicing, fabricable parts, support structure,
appearance, mechanical toy, and balancing. Applications include medicine and fashion design.
|
|
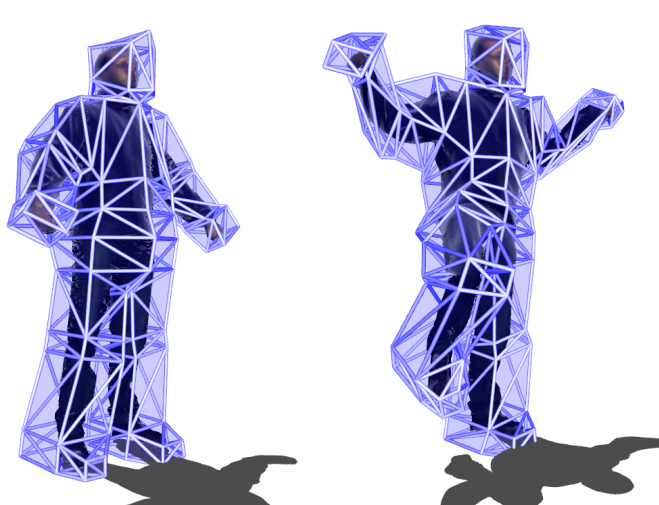
With the emergence of free-viewpoint 3DTV, we strive research effort on techniques for cage-based performance
capture. Boneless cage-based approaches is more convenient than skeleton-based approaches to guarantee non-rigid
reskinning fidelity to multi-video stream. We are interested in designing practical solutions to convert
non-rigid performance capture into cage-based animation.
|
|

|
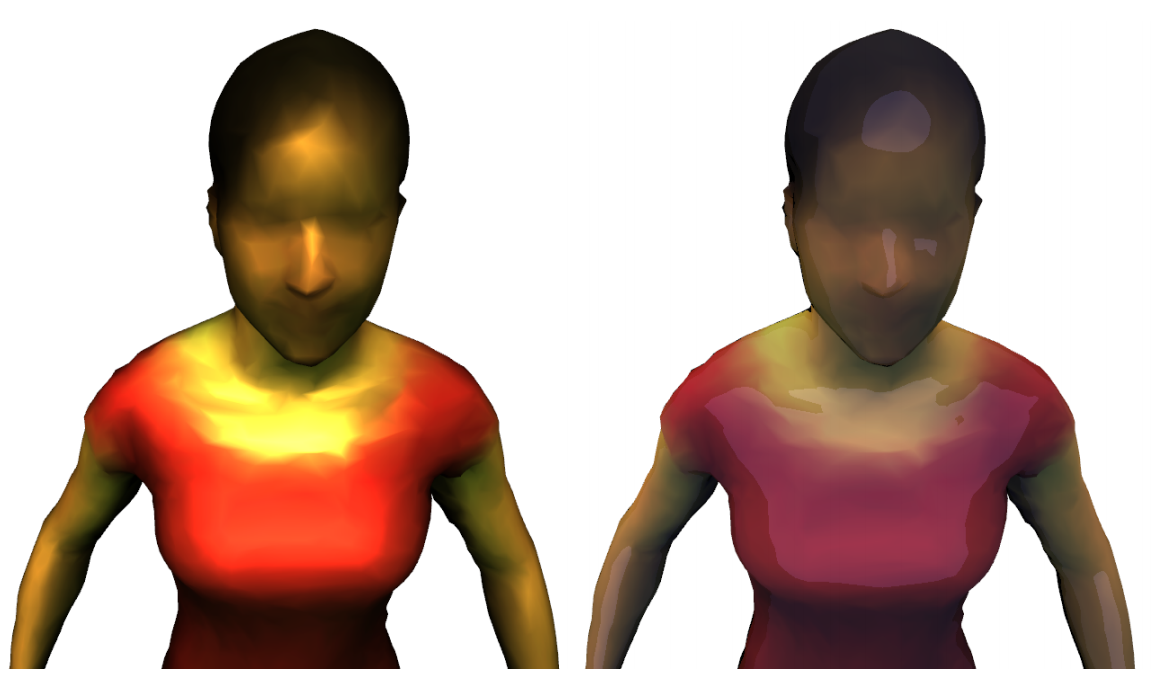
In Computer Vision, input data are gathered using sensors. Such data can be potentially reused in
post-production. In particular, cartoonization process perturbates acquired data to convey the
appearance communication in an entirely stylized delivery. We are interested to contribute in
depiction and cartoonization of captured video streams.
|
|
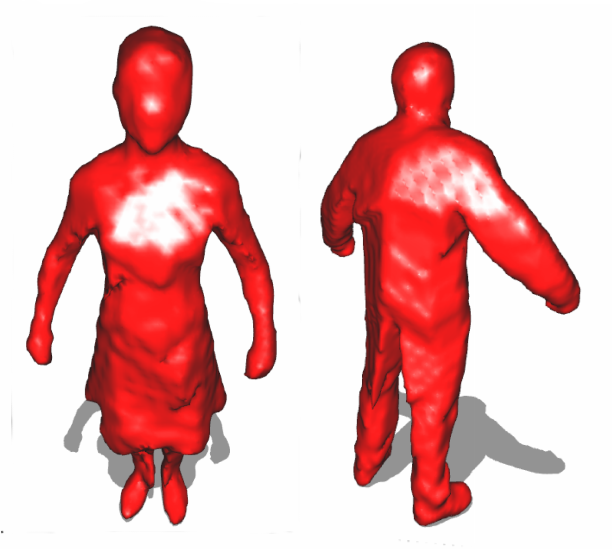
Visual hull geometric reconstruction is technique employed to improve fitting coherence of
a geometric template toward a temporal series of unstructured point clouds. In this direction, we are
interested to propose further iterative shape registration schemes only relying on skin-detached
registration strategy. Taking benefits of shape abstraction offered by low-dimensional subspaces, we
aim to develop unsupervised techniques to register life-like dynamic shapes.
|
|
|
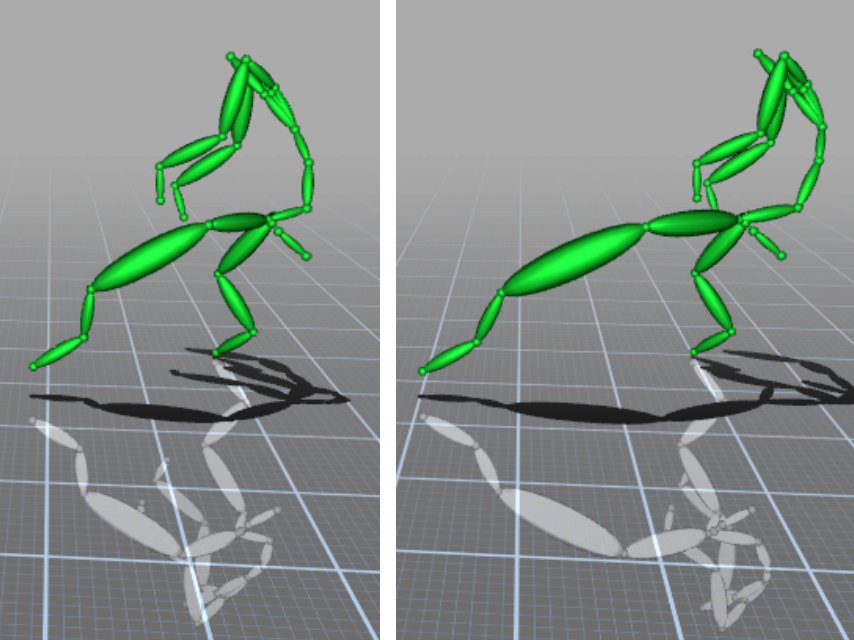
Skeletal-based structures are a classical way to animate skinned characters
using motion capture data. In particular, interactive skeletal editing allow animators to manipulate arbitrary
animation with real-time control. A problem is to enhance the expressiveness of motion clips by direct manipulation
of the underlying skeletal structure. We are interested to propose skeletal optimization for producing stretching
effects.
|
Research Interests

- Fabrication and 3D Printing
- Digital Geometry Processing
- Physical Simulation and Animation
- Performance Capture
- Computer Vision
- Computer Graphics
- Deep Learning
Past Affiliations
- Liverpool John Moores University (in United Kingdom)
- Robert Gordon University (in United Kingdom)
- University of Innsbruck (in Austria)
- Ben Gurion University of the Negev (in Israel)
- Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (in China)
- Shandong University (in China)
- FCUP Porto University (in Portugal)
- University of Bordeaux 1 (in France)
- LaBRI (in France)
- LIRIS (in France)
- University of Lyon 1 (in France)